Pelayanan Kesehatan di Kelompok Masyarakat Beresiko pada Pekerja TPST 3R Mulyoagung Bersatu Kabupaten Malang
Abstract
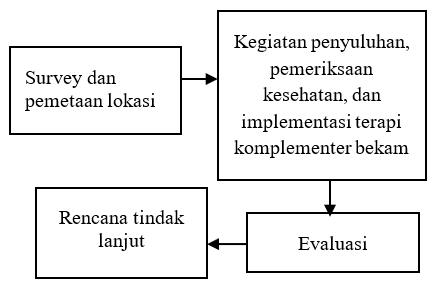
Aktivitas pekerja sampah dapat menimbulkan potensi risiko yang cukup tinggi mengingat bahaya yang dapat muncul saat kontak langsung dengan sampah. TPST 3R Mulyoagung Bersatu adalah TPST yang berada di Kecamatan Dau, Kabupaten Malang. TPST ini menerapkan pengolahan sampah masyarakat menggunakan pendekatan konsep 3R (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle). Tujuan yang ingin dicapai pada kegiatan PKM (Pemberdayaan Kemitraan Masyarakat) ini adalah memberikan edukasi kesehatan melalui pemeriksaan kesehatan dasar, penyuluhan serta pemberian terapi komplementer bekam berdasarkan kebutuhan peserta. Metode dalam menyelesaikan permasalahan mitra yakni pemeriksaan kesehatan, penyuluhan, serta pemberian terapi komplementer bekam. Hasil kegiatan PKM ini menunjukkan pekerja yang mengalami gejala klinis 13%, tingkat stres 9%, dan gangguan kualitas tidur 25% pada pre-test. Sementara hasil post-terapi keluhan gejala klinis 10%, tingkat stres 7%, gangguan kualitas tidur 20%, kepuasan terhadap terapi bekam 58%, dan rekomendasi untuk terapi bekam ke orang lain 48%. Evaluasi kepuasan pekerja terhadap terapi komplementer bekam, pekerja yang menyatakan puas 67%, rencana untuk kembali menjalani terapi 58%, dan merekomendasikan kepada orang lain 48%.
References
Baral, Y. R. (2018). Waste Workers and Occupational Health Risks. International Journal of Occupational Safety and Health, 8(2), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.3126/ijosh.v8i2.23328
Belarmino, D. V. B., Pagani, M. E. B., De Andrade Tanouye, A. T., Garcia, L. F., & Massuda, E. M. (2022). Perception of work and health among waste collectors. Revista Brasileira de Medicina Do Trabalho, 20(4), 574–581. https://doi.org/10.47626/1679-4435-2022-795
Boudanga, Z., Benhadou, S., & Medromi, H. (2023). An innovative medical waste management system in a smart city using XAI and vehicle routing optimization. F1000Research, 12, 1060. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.138867.1
Chien, S.-Y., Chuang, M.-C., & Chen, I.-P. (2020). Why People Do Not Attend Health Screenings: Factors That Influence Willingness to Participate in Health Screenings for Chronic Diseases. In International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (Vol. 17, Issue 10). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103495
Di Renzo, L., Gualtieri, P., & De Lorenzo, A. (2021). Diet, Nutrition and Chronic Degenerative Diseases. In Nutrients (Vol. 13, Issue 4). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041372
Dirjen Pelayanan Kesehatan. (2022). Penyakit Akibat Kerja (PAK). Kementerian Keseahatan RI. Jakarta. https://yankes.kemkes.go.id/view_artikel/787/penyakit-akibat-kerja-pak
Fauzi Tanjung, Q., & Ishadi, H. (2022). The Medical Perspective of Dry Cupping and Wet Cupping: Effects and mechanisms of action. Journal of Society Medicine, 1(1), 31–35. https://doi.org/10.47353/jsocmed.v1i1.6
Ferronato, N., & Torretta, V. (2019). Waste Mismanagement in Developing Countries: A Review of Global Issues. In International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (Vol. 16, Issue 6). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16061060
Hassan, S. A., Mohamed, F., Sheikh, N., Basualdo, G., Daniel, N. A., Schwartz, R., Gebreselassie, B. T., Beyene, Y. K., Gabreselassie, L., Bayru, K., Tadesse, B., Libneh, H. A., Shidane, M., Benalfew, S., Ali, A., Rao, D., Patel, R. C., & Kerani, R. P. (2021). "They Wait until the Disease Has Taking over You and the Doctors Cannot Do Anything about It": Qualitative Insights from Harambee! 2.0. In International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (Vol. 18, Issue 23). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312706
Kim, S., Lee, S. H., Kim, M. R., Kim, E. J., Hwang, D. S., Lee, J., Shin, J. S., Ha, I. H., & Lee, Y. J. (2018). Is cupping therapy effective in patients with neck pain? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open, 8(11), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-021070
Mehta, P., & Dhapte, V. (2015). Cupping therapy: A prudent remedy for a plethora of medical ailments. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 5(3), 127–134. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2014.11.036
Oza, H. H., Lee, M. G., Boisson, S., Pega, F., Medlicott, K., & Clasen, T. (2022). Occupational health outcomes among sanitation workers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 240, 113907. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.113907
Stol, Y. H., Asscher, E. C. A., & Schermer, M. H. N. (2017). What is a good health check? An interview study of health check providers' views and practices. BMC Medical Ethics, 18(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-017-0213-x
Thai, T., Kučera, P., & Bernatik, A. (2021). Noise Pollution and Its Correlations with Occupational Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Cement Plants in Vietnam. In International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health (Vol. 18, Issue 8). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084229
Wu, L.-K., Chen, Y.-C., Hung, C.-S., Yen, C.-Y., Chang Chien, C.-Y., Ciou, J.-R., Torng, H.-H., Chang, Y.-C., Hua, S., Lu, P.-N., Liu, Y.-Y., Lai, C.-Y., Kung, Y.-L., Huang, H.-K., Chen, Z.-K., & Ho, T.-J. (2023). The efficacy and safety of cupping as complementary and alternative therapy for metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine, 102(13). https://journals.lww.com/md-journal/fulltext/2023/03310/the_efficacy_and_safety_of_cupping_as.1.aspx

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.














